Infertility refers to the condition where a woman cannot get pregnant. Hormonal imbalance most often causes infertility. It’s a distressing situation for both men and women.
Some cases are treatable while others are not. In this article, we’ll look at various causes of infertility in women and how to manage or treat them.
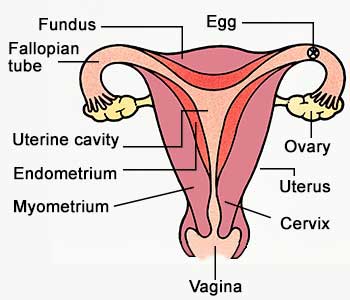
Since we’ll refer to various parts of the female reproductive system, this picture will help you get a basic understanding:
Hormones That Are Involved In Pregnancy
Without going too deep into the science of hormones and pregnancy, you should have a basic understanding of the hormones involved in pregnancy in order to address the problem.
The following hormones control pregnancy:

- Thyroid hormones – the thyroid gland produces a lot of hormones, but triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) hormones are involved in production of prolactin.
- Prolactin – milk production is controlled by prolactin. This hormone also plays an essential role in becoming pregnant in the first place. If you have low levels of prolactin, you’re likely to have irregular cycles and issues with ovulation, which can interfere with getting pregnant.
- Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) – This hormone supports the immature eggs. Ovarian follicles, or the sack that contains the immature egg, produce AMH.
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) – FSH helps regulate the menstrual cycle and induce the production of eggs in the ovaries.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) – LH signals the body to release a mature egg.
- Progesterone – This hormone is essential to maintaining a pregnancy by thickening the uterine lining, which in turn helps support an embryo. Women with low progesterone levels often experience recurrent miscarriages.
- Estrogen – Low estrogen levels can prevent ovulation and make getting pregnant difficult, leading to infertility.
Signs & Causes Of Hormonal Imbalance
The most common signs of hormonal imbalance in women include:
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Spotting or irregular bleeding
- New or worsening acne
- Facial hair
- Male-pattern body hair
- Male-pattern hair loss
- Unexplained weight gain
- Extreme mood changes
Hormonal imbalance is usually caused by dysfunction of the thyroid gland, or Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), discussed in more detail below.
What Causes Infertility In Women?
There are various causes of infertility in women, and sometimes the cause remains unknown.
Here are the most common causes:
1) Infrequent Release Of Eggs From The Ovary:
This can happen as a result of various physical or medical conditions, such as
- General illnesses
- Hormonal imbalance – such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Being overweight
- Losing too much body weight
- Premature ovarian failure or early menopause – this happens when the ovaries stop producing eggs before the age of 40.
2) Short Luteal Phase
The first day of your period starts the follicular phase, when the ovaries prepare to release an egg to the fallopian tube.
The luteal phase is the time period that immediately follows ovulation. The follicle in your ovary that contained the egg before ovulation changes into the corpus luteum whose function is to secrete progesterone.
Progesterone controls the luteal phase, and maintains the thickness and strength of uterine wall to maintain a pregnancy.
If your body doesn’t secrete enough progesterone, the uterine lining doesn’t properly develop. This makes it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant in the uterus.
The luteal phase is typically 13 to 14 days on average. If your luteal phase is less than 10 days, a fertilized embryo may not be able to implant, preventing pregnancy.
A short luteal phase can also be due to the failure of the corpus luteum.
If the corpus luteum doesn’t secrete enough progesterone, your uterine lining may shed before a fertilized egg is implanted. This can cause an earlier menstrual cycle.
A short luteal phase can also be caused by
- Anorexia
- Obesity
- Aging
- Excessive exercise
- Stress
- Too much of the hormone prolactin – responsible for milk production
- Underactive or overactive thyroid
- Endometriosis (discussed below)
- PCOS (discussed below)
How To Treat Short Luteal Phase
- Progesterone supplementation: – The most common treatment for a short luteal phase is to give the woman extra progesterone to prevent the loss of a pregnancy. Usually, progesterone supplementation is begun three days after ovulation.
- Lowering your body mass index (BMI): – Effective if the underlying reason is obesity. BMI is a measure of body fat based on height and weight. A lower BMI leads to a healthy body composition, where your body has a lower percentage of body fat and a higher percentage of non-fat mass.
- Easy to moderate exercise: – Effective when stress or exercise are causing a problem
GOT QUESTIONS?

Get A Free Expert Consultation
Navigating supplements without professional help can be expensive and dangerous. We are here to help.
There’s no obligation.
3) Problems In The Womb
These are problems such as:
a) Uterine Fibroids:
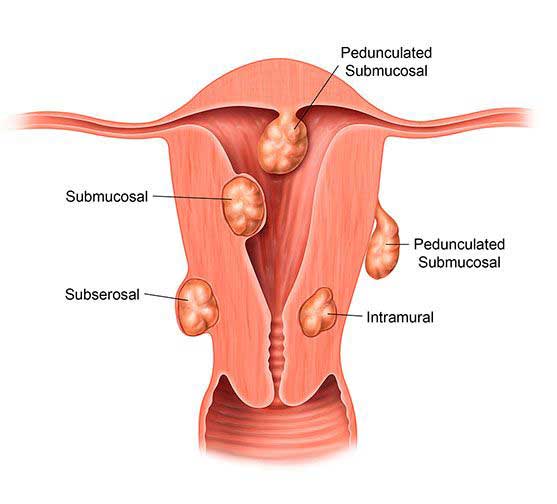
Uterine fibroids are lumps that develop from the muscle wall of the womb (myometrium). Fibroids that sit or project inside the womb cavity are particularly known to cause infertility.
Fibroids can develop due to hormonal imbalance – if estrogen levels are too high. If you don’t have sufficient progesterone, the body can’t stop the growth.
Progesterone limits the effects of estrogen on fibroids, and also deters their growth and limits their size.
Studies also find that diets high in red meat and fats, especially animal fats, have been shown to increase the risk of fibroids and risk factors for fibroids, including high blood pressure.
Aim for a diet high in flavonoids, oily fish, green vegetables, fruits, and beans.
How To Treat Fibroids:
- Surgery: – Your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the fibroids or cut blood supply to them.
- Lowering your BMI: – Weight / obesity has been shown to increase the risk of developing fibroids. Consider getting into ketosis to manage your weight. Our KETO XP supplement can help you get into ketosis.
- Diet: – Avoid red meat, alcohol, refined carbs (such as rice, flour, etc), baked goods. Good foods are fruits and vegetables, whole grains, quinoa, etc.
- Health supplements: – Low levels of vitamin A and D have been related to the risk for developing fibroids. Others are vitamins B-1, B-6, and E, as well as magnesium and omega3 fatty acids. DIM can also help with fibroids.
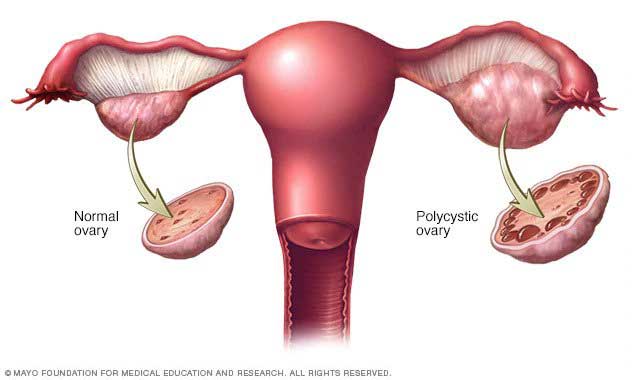
b) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal condition in which the ovaries develop numerous small collections of fluid (follicles) and fail to regularly release eggs.
Even though the exact cause is not known, PCOS seems to be caused by environmental factors as well as genetics.
Women with PCOS may have infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods or excess male hormone levels such as testosterone.
PCOS leads to fertility problems, weight gain, acne, and unwanted hair growth
It also leads to a condition where cells don’t respond well to the release of the hormone that breaks down glucose (insulin) – hence they can’t use the glucose they need for energy.
In response, the pancrease keeps making more and more insulin. Eventually the pancrease fails, leading to diabetes.
The extra insulin may have several negative effects including shutting down your ovaries and leading to higher than normal levels of male hormones, called androgens, including testosterone. Testosterone can interfere with normal ovulation, leading to fertility problems.
How To Treat PCOS:
- Exercise: – Exercise builds muscle, thereby improving glucose metabolism. In fact, exercise is the only treatment that improves all markers of metabolic syndrome.
- Lowering your BMI: – Many women with PCOS are overweight. Losing just 5 percent of their body weight can restore regular ovulation and menstruation and improve fertility.
- Herbal supplements: – V. chasteberry has been very promising in treating PCOS. Other supplements like cinnamon, black cohosh, Tribulus terrestris, licorice, and Chinese peony, also show some benefits.
- Medication: – Doctors will prescribe oral contraceptives to improve ovulation and reduce the potentially dangerous effects of too much estrogen on the uterine lining. If this doesn’t work, the drug metformin can reduce the amount of glucose the liver releases, and increases the amount of glucose absorbed in the intestine. This can restore ovulation in 30-50% of women with PCOS.
4) Endometriosis
In endometriosis, uterine tissue grows outside the uterus, which can lead to cysts being formed in the ovaries and the pelvis. This can cause the fallopian tubes to become distorted which, in turn, can lead to infertility.
Endometriosis can also be caused by high levels of estrogen.
Common signs of endometriosis include:
- Painful periods
- Pain during intercourse
- Heavy menstrual periods and bleeding between periods
- Infertility
How To Treat Endometriosis:
The conventional treatment for endometriosis involves pain medication, hormonal therapy, or surgery.
In some cases, hysterectomy with removal of the ovaries is done.
Health supplements can also be effective in treating endometriosis, such as:
- DIM (diindolylmethane): – DIM, is anti-inflammatory in nature, and is metabolized similarly to estrogen. Because of this, in low doses, it may help promote healthy estrogen breakdown and removal from the body.
- Vitamin B6: – It is possible that vitamin B6 might play a role in hormone regulation. Through a complex pathway, vitamin B6 may reduce the level of estrogen in the body, potentially relieving endometriosis-related symptoms.
- Curcumin (turmeric):– Research on curcumin for the treatment of endometriosis is limited, however, several studies and reviews have suggested that it may provide relief from endometriosis-related symptoms.
5) Blockage Of One Or Both Fallopian Tubes:
5) Blockage Of One Or Both Fallopian Tubes:
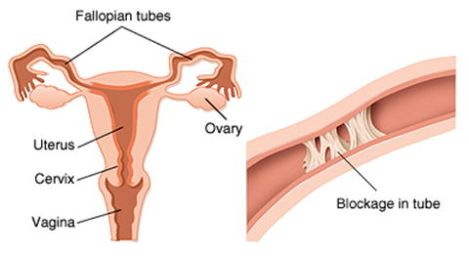
This can happen through
- Infection – such as Chlamydia, which is a sexually transmitted disease
- Pelvic adhesions caused through surgery or through non-tubal infection (such as appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease)
- Endometriosis, which can cause a tissue buildup in the tubes
- Pelvic inflammatory disease, a disease that can cause scarring
- Fibroids, which are growths that can block the fallopian tube
Summary
I know this post contains a lot of information about how hormonal imbalance relates to infertility. It’s hard to capture everything in one post, especially given that every woman’s situation may be unique.
Getting a basic understanding of how hormones relate to fertility and women’s health will help you address the specific problem preventing pregnancy.